Organic acids can be analyzed with capillary electrophoresis using direct or indirect UV detection. Depending on the pH of the electrolyte the dissociation of the acids can be modified and therefore selectivity of the separation can be optimized. Additionally selectivity can be enhanced using specific cations as additives due to their influence on the solubility behavior. The addition of organic modifier can also be used to improve the separation of organic acids with CE.
Organic Acids with direct UV detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: 50 mM Borate
- Capillary: Polybren coating, Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
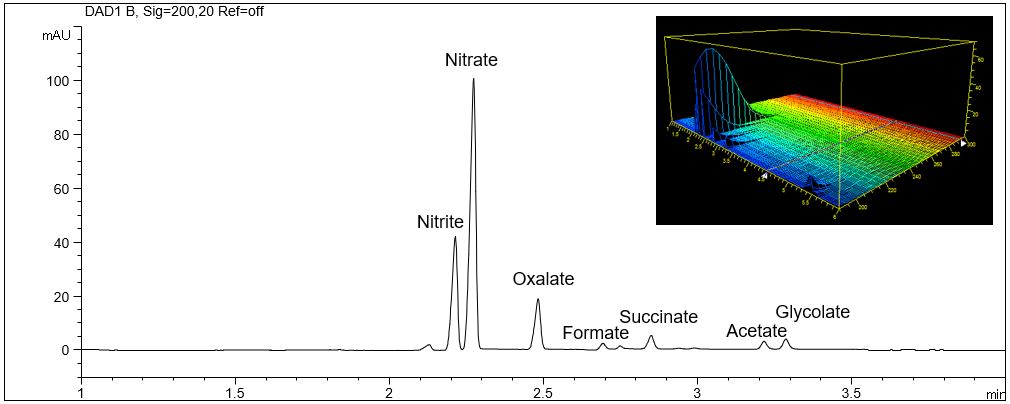
- Description: Aliphatic organic acids can be analyzed with direct UV detection due to the UV absorption of the carbonyl group. Unfortunately, the resulting extinction coefficients are small. As the concentration of organic acids in real samples is usually very high this method is normally sufficient for the demanded sensitivity. The given example shows the separation of a selection of different organic acids as well as anions like nitrate and nitrite, which are very sensitive due to their high extinction coefficients. The 3D-plot of the electropherogram shows the different absorption of the peaks. Anions like chloride or sulfate can not be analyzed with this method.
Download: organic acids direct detection
Organic acids in strawberries using direct UV detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 8.5
- Capillary: PVA coated, 50 µm I.D., bubble cell, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 15 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Three fruits of each sort were pureed and deep-frozen. Immediately before the measurement, the puree was thawed. Each puree was diluted 1:5 using water and centrifuged to separate insoluble solids.
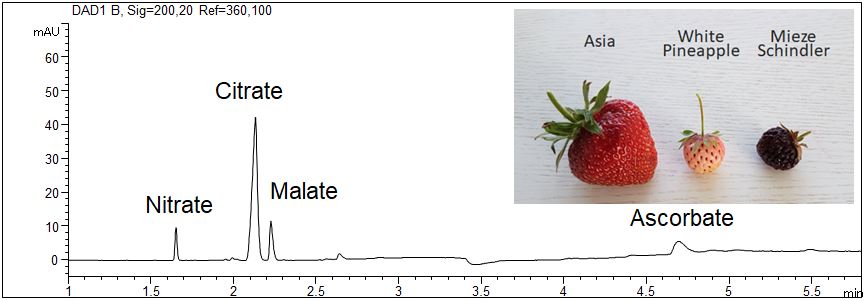
Acids in eight sorts of strawberries
It was found that citric acid and malic acid are the main organic acids in strawberries. The content and the relation of citrate and malate differs in the different sorts of strawberries. White Pineapple shows the highest content of organic acids and Vima Zanta the lowest. The content on nitrate could be caused by fertilization or by the degradation of amino acids.
Download (426 kB): strawberries-acids.pdf
Organic acids in fruits using direct UV detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 8.5
- Capillary: PVA coated, 50 µm I.D., bubble cell, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 15 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: In the PDF (196 KB) the e-grams of the organic acids of a standard solution, tangerine, and two sorts of strawberry are shown. The standard solution contains the following analytes: nitrite, nitrate, citrate, malate, acetate, salicylate, aspartate, glutamate and ascorbate. In the fruits high amounts of citrate and malate were detected.
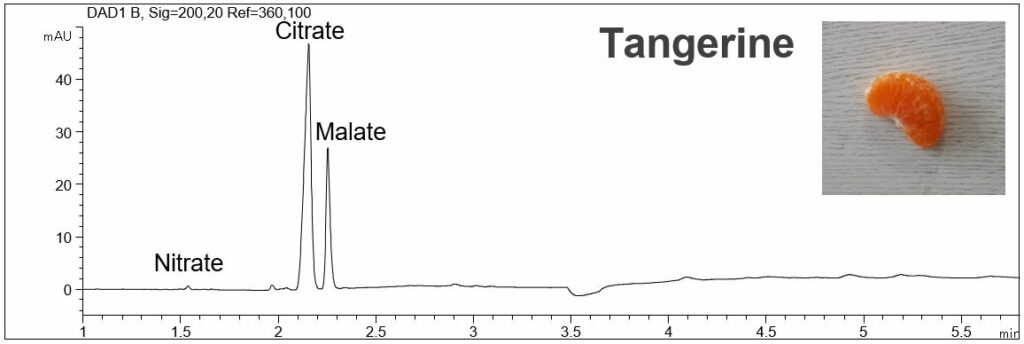
Organic acids in fruits (tangerine, strawberries)
Download (196 kB): org-acids-fruits.pdf
Mandelic acid with direct UV detection
Synonyms: 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylethanoic acid, α-Hydroxybenzeneacetic acid, Almond acid, Mandelsaeure, CAS: 90-64-2
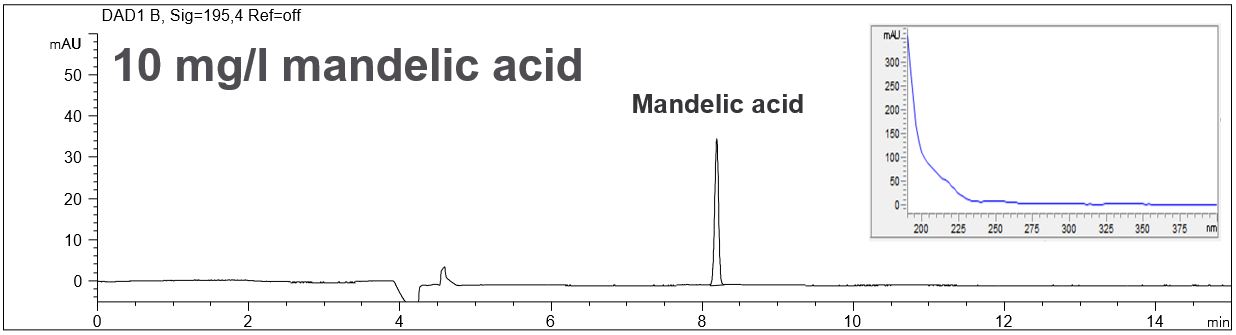
Mandelic acid C8H8O3 is often used in cosmetic products for skin care and it is a useful precursor to various drugs. Mandelic acid has an aromatic structure and can therefore be measured with direct UV detection with high detection strength. It can be determined co-electroosmotic and therefore the use of an EOF modifier is not necessary.
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate, SDS
- Capillary: 50 µm I.D., fused silica, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 195 nm
- Description: In the PDF the electropherograms of standard solutions, the spectral data of the peak and LOD and LOQ can be seen.
Download: Mandelic acid
Organic Acids with indirect UV detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Basic Anion Buffer pH 12.1 (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 114 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
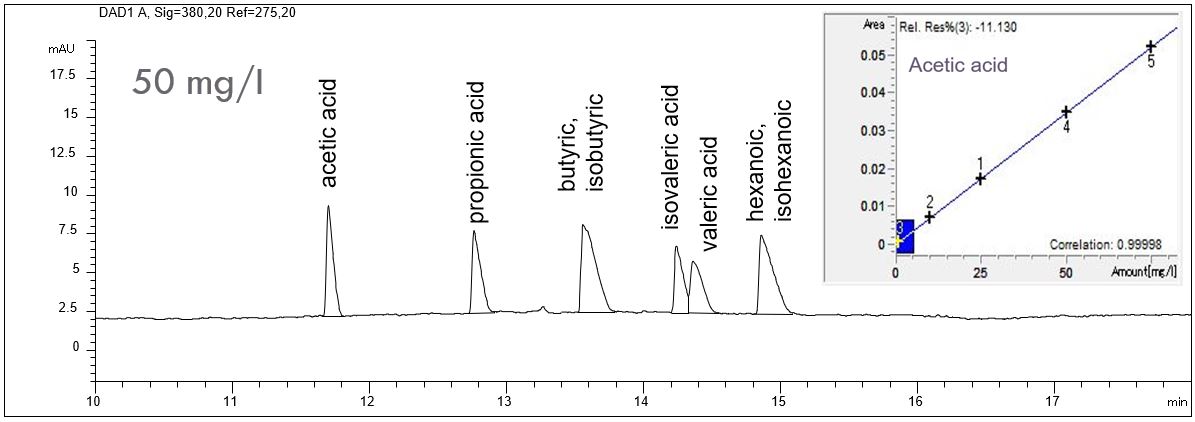
- Description: The separation of aliphatic organic acids with indirect UV detection is possible when the electrolyte contains a modifier which shows high UV absorption as well as a substance which reverses the EOF mobility in the capillary. High pH value of the electrolyte guarantees deprotonation of the organic acids. All these conditions are met by the Basic Anion Buffer from Agilent. The two-sided PDF shows a standard solution of organic acids in different concentrations as well as the calibration lines.
Download: Organic-acids-indirect.pdf
Amino Acids with direct UV detection
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate/SDS
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
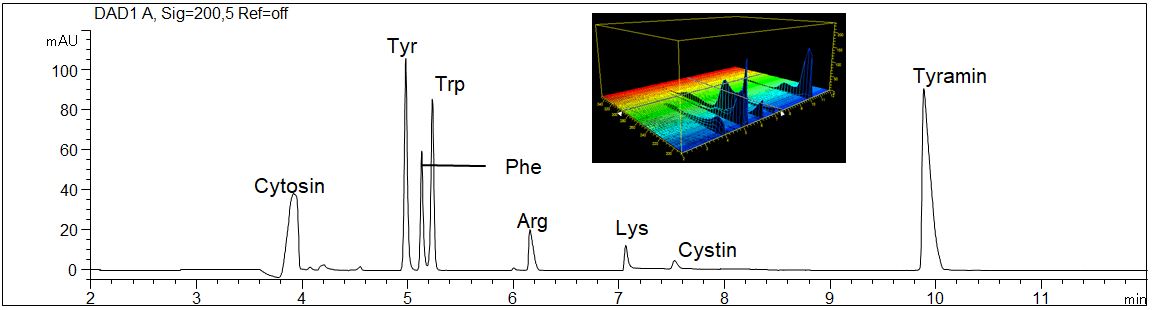
- Description: The separation of eight amino acids in a standard solution as well as the 3D UV spectra is shown.
Download: Amino-acids.pdf